Flexible electronics have found a wide variety of novel applications such as flexible displays, flexible solar cells, flexible circuits, electronic papers, and touch screens. Recently, it can be seen that several studies have conducted to explore high density flexible energy storage devices for their potential applications in flexible electronics such as electronic displays, mobile phones, smart bands, health bands, laptops, and computers [1].
Heteroatom-doped graphene electrodes have found to be one of a promising candidates for high density flexible energy storage applications due to its dual nature of pseudo capacitance and electrochemical double-layer capacitance. Moreover, the low energy density supercapacitors limits its potential usage and the attempts are still in progress to overcome this problem. To augment for the high energy density of the supercapacitor device, the redox-additive electrolytes are believed to be one of the elite tactics. Here, they have reported on sodium molybdate (Na2MoO4)-incorporated polymer gel electrolyte to enhance for the energy of high density of a flexible supercapacitor. The supercapacitor electrode with Na2MoO4/H2SO4 (714 F/g) were acquired of ∼2.4-fold greater with its specific capacitance than with H2SO4 (300 F/g) in a three electrode configuration. The fabricated flexible supercapacitor device with sodium molybdate along with poly(vinyl alcohol)/sulfuric acid (Na2MoO4/PVA/H2SO4) gel electrolyte have showed 3.4-fold higher energy density. Hence, the increase in the energy density was due to the incorporation of Na2MoO4, and the faradaic reaction between MoO42− ions and the redox-additive of H+ ions in the H2SO4 electrolyte [2].
Graphene has gathered greater attention for the supercapacitor applications owing to its high mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and specific surface area. Recent studies have shown that the graphene could be an ideal electrode material by utilizing its entire surface area, due to its ability to store for EDLC (electrochemical double-layer capacitance) [3, 4].
Supercritical fluid (SCF) processing is found to be one of the best synthetic methods due to its advantages such as one-pot synthesis within a short reaction time. Moreover, SCF possesses some unusual properties like gas-like diffusivity, viscosity, and low density that are essentially required to increase the homogeneity and porosity of the materials.
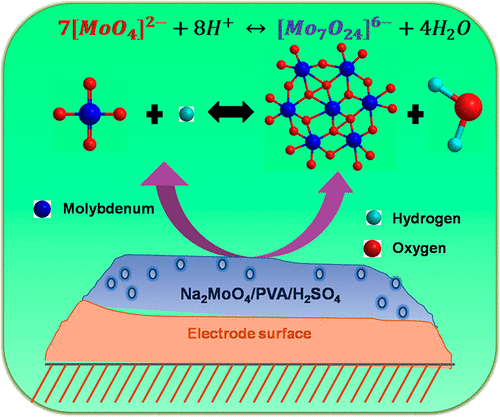
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of sodium molybdate along with poly(vinyl alcohol)/sulfuric acid (Na2MoO4/PVA/H2SO4) gel electrolyte for high energy density supercapacitors [1].Over the past few years, various research attempts have been made to increase the energy density of the supercapacitor devices. The primary key advantage of using the redox additives are facile and safe with acidic, basic, and neutral electrolytes at its room temperature without any special care. The redox additives are classified into two categories viz., (i) organic and (ii) inorganic additives, respectively. Generally, anthraquinone and hydroquinone are used as organic redox additives which are caused by the redox reaction between the additives and the electrolyte with the existence of pseudo capacitance. It can also be seen that, the inorganic redox additives like CuS, KI, and K4Fe(CN)6 were found to be relatively more attractive due to their low cost and improved cyclic performance. Also, they have reported that MoO42− species of Na2MoO4 in the presence of H+ ions could be readily transformed into a polymeric form of H2MoO4 which will be participates in the redox reaction [5].
The redox additives such as Na2MoO4, KI and ferrous ammonium sulphate (FAS) can be used with conventional H2SO4 electrolyte which was found to be one of the best approach to augment for the specific capacitance and dynamic potential window of the carbon-based electrode materials. After the addition of Na2MoO4 with H2SO4, there is no any appreciable change in the capacitance retention which may be suggested that the faradaic reaction between the MoO42− and H+ ions in the electrolyte does not affect the stability of the electrode. Moreover, after the addition of Na2MoO4 with PVA/H2SO4 polymer gel electrolyte, there is an increase in the capacitance retention which could be predominantly due to the faradaic reaction between MoO42− ion in the redox additive and H+ ions in the electrolyte. Also, surprisingly, it has provide the additional stability to the flexible devices and the redox reaction of polymeric H2MoO4 which does not affect the stability of the electrode [1].
A special attention on a bendable and flexible supercapacitor device for the flexible electronic device applications have been seeking in this modern era civilization. To fabricate a flexible and bendable supercapacitors, numerous efforts have been initiated recently. Hence, for the fabrication of mechanically stable flexible supercapacitor, the graphite sheets are used as a current collector. Moreover, the electrolyte and current collectors are the two main key components for the advancement of flexible devices. In addition, the redox-additive incorporated polymer gel electrolyte will function as an electrolyte and separator as well. Hence, this can be simplify the fabrication process and will reduce the weight of the flexible devices [6].
Our SNB team have emphasize this research article to enrich our viewer’s knowledge about the high density flexible supercapacitors via polymer gel electrolyte. It can be seen that the commercial applications for the supercapacitor may generally prefer many flexible devices that are connected with series or parallel to meet the requirement with higher operating currents or voltages. Further, they have investigated that the performance of a capacitor pack with three flexible supercapacitors are connected in series. Hence, it is noteworthy that the flexible supercapacitor can be easily processed for the large-scale production with a simple fabrication process using polymer gel electrolyte with high energy density. Thus, the fabricated flexible supercapacitor with Na2MoO4 redox additive via polymer gel electrolyte could be easily scaled-up for commercial applications and can be applicable for flexible portable devices which is an evitable one in the near future.
References
- M. Sandhiya et al., ACS Appl. Energy Mater (2020), https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.0c02299.
- W. K Chee et al., J.Phys. Chem. C, 120, 4153 (2016).
- S. Park et al., Nanoscale 5, 1727 (2013).
- Y. Shao et al., Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 3639 (2015).
- D. Xu et al., J. Power Sources, 341, 448 (2017).
- W. Li et al., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 55, 9196 (2016).
--- Dr. Y. Sasikumar
School of Materials Science and Engineering
Tianjin University of Technology, China

Comments
Post a Comment