Pesticides have played a remarkable role in the human health issues towards our life and security scenarios. Pesticides are gaining new attention to protecting our livestock and crops from pests, weeds, nematodes and insects. Preferably, the carbamates contained pesticides are utilized in gardening, agriculture, forestry and therapeutic pharmaceuticals, at simultaneous to minimal nonpersistence and bioaccumulation in the present environmental needs [1].
A specific and most toxic one is carbofuran (CF) also called as 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl N-methyl carbamate, a compound which belongs to the carbamate pesticides family [2].
Stability Analysis and Determination of CF, Interference:
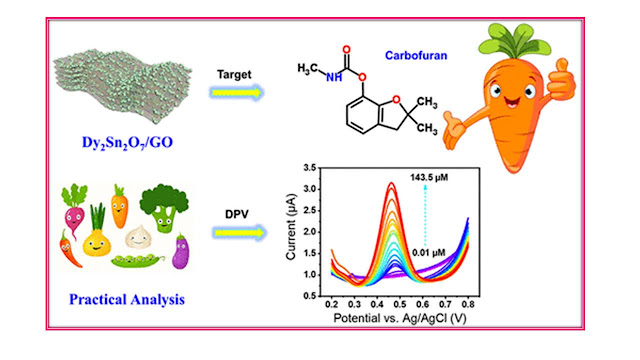
For the potential real-time analysis, the practical investigation of CF is significantly important for CF in the environmental samples. Hence, the study of detection level of CF should be done. For the estimation of detection level of CF, the DPV was performed with Dy2Sn2O7/GO composite electrode for the detection of various concentrations of CF. It can be seen that the results have showed that oxidation peak current gets gradually increased with consecutive excess additions of CF in the concentration level of 0.05-143.5 μM. Furthermore, the results revealed that the Dy2Sn2O7/GO composite was found to be superior electrocatalysts with an excellent electrocatalytic activity and potential candidate for the low-level analysis of CF in the environmental samples. The Dy2Sn2O7/GO composite was found to be ultrasensitive with low-level detection candidate for the analysis of CF based upon these results.
The anti-interference effect of CF with Dy2Sn2O7/GO electrode was investigated by DPV, are conducted in the presence of 25 μM CF and 50-fold excess concentration of cations of calcium (Ca2+), cadmium (Cd2+), magnesium (Mg2+), copper (Cu2+), and iron (Fe3+) with 20-fold excess concentration of ascorbic acid (AA), carbendazim (CBZ), malathion (MTN), caffeic acid (CAF), aminophenol (AP), parathion (PTN), 2,4,6,-trichlorophenol (2,4,6-TCP), and thiamethoxam (TMN). It can be observed that while adding the excess concentration with other interfering compounds, there is no any disturbance in the oxidation peak current, and the relative error was found to be ≤5% which indicates that the Dy2Sn2O7/GO was the suitable electrocatalyst for the real-time analysis of CF for the practical applications. For the determination of the capability of the proposed electrode, repeatability and operational storage stability of the Dy2Sn2O7/GO electrode were also been investigated in addition. For the repeatability examination, DPV were carried out for the Dy2Sn2O7/GO electrode performed with 10 continuous measurements in N2-saturated 25 μM CF containing PBS, pH 7.0. It can be observed that stability of the anodic peak current was slightly decreased after 10 measurements, with a relative error of ≤2.3%. This indicates the acceptable repeatability level of the Dy2Sn2O7/GO electrode for the consecutive analysis of CF. Also the operational storage stability of the Dy2Sn2O7/GO electrode was tested in N2-saturated 25 μM CF containing PBS, pH 7.0 [5]. Hence, the results showed that a minor variation in the oxidation peak current for the developed electrode after an interval of 20 days. Therefore, the proposed Dy2Sn2O7/GO electrode offers unique electrochemical properties with an excellent operational stability for the CF detection.
Real-Time Analysis of CF:
DPV was conducted with Dy2Sn2O7/GO electrode for the vegetable samples using a standard addition method for the real-time practical analysis. The process for the preparation of vegetable extracts was the top layer skin peeled off, dried, and crushed finely from the vegetable samples. Extractions of the crushed samples were mixed with 0.1 M of sodium hydroxide for the hydrolysis. It can be seen that the results showed no current response of CF for the vegetable extract which have used with supernatant solutions. The vegetable samples are ranged from 96.5 to 99.9% with RSD less than 1.72 was the outcome recovery of CF. This revealed that the Dy2Sn2O7/GO composite electrode is a required candidate for the low-level analysis.
Our SNB team have emphasize this research article to help the reader to know about the development of a low cost, with a very sensitive approach for the determination of toxic CF in vegetable samples for real-time application. The presence of an effective composite lead be formulated to avoid the fouling of the electrode surface, to enhance the charge transfer rate, to improve electrocatalytic activity towards the electrochemical analysis of CF. Beyond the preparation of hybrid composite materials and characterizations, this research team have pointed out the fast electron migration over the interface (electrode-electrolyte). The performance of Dy2Sn2O7/GO materials are monitored by techniques (CV, DPV) and expressed with effective electrocatalytic activities (high concentration, scan rate, pH levels, high storage stability) towards the identification of CF. In addition, the real-time sample analysis of vegetable samples (cabbage, potato, carrot, eggplant) are compared with relative standard deviation analysis. Hence, the above conclusions and suggestions in this content will be guiding us from the prediction of CF for the future challenges.
References:
- S. Mishra et al., Chemosphere 2020, 259, 27419
- S. Sun et al., Curr. Pollut. Reports 2018, 4, 240.
- B. Thirumalraj, et al., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 8, 48, 17882 (2020), Doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07973.
- P. Veerakumar et al., J. Electroanal. Chem 2018, 826, 207.
- M. Velmurugan et al., J. Colloid
Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 123.
--- Dr. K. Rajkumar
Email:drcrystalphd@gmail.com

Comments
Post a Comment